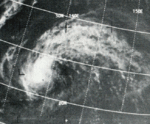
The 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season was an exceptionally active Pacific tropical cyclone season which featured numerous tropical cyclones affecting the Philippines, China, and Vietnam. Despite the first half of the year being entirely dormant of any tropical cyclone activity, from June onwards, various factors led to the season becoming extremely deadly and destructive. As a whole, the basin produced 30 total tropical depressions, all of which further intensified into tropical storms. Twenty-one of the tropical storms became typhoons, and a record-tying eleven typhoons reached super typhoon intensity, an unofficial category created by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC).
Many destructive storms formed during the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season. First, in early August, Typhoon Faith became one of the costliest storms to strike the Philippines on record, causing an estimated $2 billion (2029 USD) in losses and resulting in 666 deaths. Next, in mid-August, Typhoon Hope became one of the worst natural disasters to ever impact Taiwan, killing 503 people and causing an estimated $1 billion (2029 USD) in damage. Third, Typhoon Juliet, forming only a few days after Hope, further contributed to the storm's impact on Taiwan and brought very high ocean waves along the Mainland China coastline, resulting in 123 fatalities and total damages of $1.7 billion (2029 USD). Fourth, in late September, Typhoon Quinn became the strongest, costliest, and deadliest Planet X tropical cyclone ever, reaching maximum 10-minute sustained winds of 185 miles per hour (mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 854 millibars (mbar), as well as assaulting the Philippines, Vietnam, Hainan, Taiwan, and the Shanghai metropolitan area. All in all, the typhoon caused approximately 300,000 deaths and damages of up to $200 billion (2029 USD). Fifth, in early October, Typhoon Sukru added on to the misery left behind by Quinn; not only did it affect the Philippines, but it made landfall near Hong Kong, affecting the administrative region as well. In the typhoon's aftermath, an estimated 40,000 fatalities were reported, and losses of up to $3 billion (2029 USD) were reported. Sixth, in mid-October, just weeks after Quinn and Sukru, Typhoon Ulli affected the Philippines, Hong Kong, Macao, and several major metropolitan areas in Mainland China, killing 7,000 people and left $1.1 billion (2029 USD) in damage. Finally, in early November, Typhoon Antoinette affected Vietnam and later became one of the deadliest Philippine typhoons on record, causing 1,143 deaths and $90 million (2029 USD) in losses. Despite China, the Philippines, and Vietnam receiving the brunt of the landfalls during the season, most of the other regions in the basin prone to landfalls, such as Japan and the Koreas, escaped the destructive storms. Collectively, the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season resulted in total losses of roughly $209.265244 billion (2029 USD) and an estimated 351,564 total fatalities, both of which represent record highs for the West Pacific tropical cyclone basin.
The scope of this article covers the tropical cyclones which form in the Pacific Ocean and its neighboring seas that lie north of the Equator and west of the International Date Line. Should a tropical cyclone form north of the Equator but to the east of the International Date Line, it is called a hurricane, not a typhoon. Once a tropical depression forms in the Western Pacific, the JTWC assigns a number and adds a "W" suffix to it, and the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) assigns a six-digit number as well; the first four digits represent the year it formed in, and the last two digits represent the nth storm of the season the JMA has tracked. Should a tropical depression further intensify into a tropical storm, the JTWC will assign the storm a name from a predetermined naming list. Also, if a tropical depression forms or enters the area of responsibility monitored by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA), the agency will assign a name from its own predetermined naming list to the system. Consequently, it is possible for one single storm to have two different names, one assigned by the JTWC and the other by PAGASA.
Seasonal forecasts[]
| Source | Date | Total TCs |
Tropical storms |
Typhoons |
| JMA | Average (2015-2030) | – | 24 | 13 |
| JTWC | Average (2015-2030) | 29 | 25 | 15 |
| JMA | April 4, 2029 | – | 30 | 20 |
| JMA | Actual activity | 30 | 30 | 21 |
| JTWC | Actual activity | 30 | 30 | 21 |
On April 4, 2029, meteorologists at the JMA issued the agency's first ever seasonal forecast for the upcoming 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season. Citing the extremely strong El Niño conditions across the Western Pacific, the JMA predicted 30 total storms and 20 total typhoons would form during the season, with a margin of error of 7 and 6, respectively. Although the predicted number of storms perfectly verified, the number of typhoons was very slightly underestimated, as 21 total typhoons developed throughout the year.
Seasonal summary[]
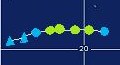
Timeline of tropical activity in the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season


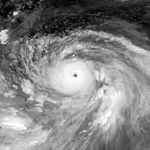
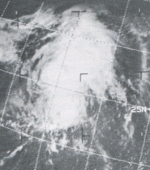
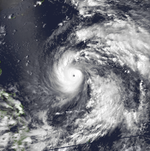
In this photo, Typhoon Quinn, the season's strongest and most destructive storm, is exhibiting characteristics of an annular tropical cyclone. It is also at a Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale (SSHS) rating of Category 5 super typhoon intensity in this image.
For the entirety of the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season, the JMA, headquarted in Tokyo, issued advisories on all systems that formed in the Pacific Ocean north of the Equator, west of the International Date Line, and east of the Malay Peninsula. This season marked the first time the JMA had been given this privilege; the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) designated it the Western Pacific tropical cyclone basin's official Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC). In previous years, the JTWC, located in Pearl Harbor, was the basin's official RSMC; however, the WMO decided to pass on the designation to the JMA from 2029 onwards.

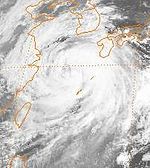
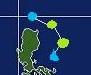
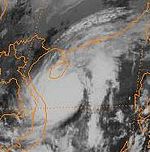
In this photo, Typhoons Ulli and Vera are executing a Fujiwhara interaction. Both storms are of Category 5 intensity on the SSHS.
Nevertheless, the JTWC continued issuing unofficial advisories on the season's systems. The JMA and the JTWC both issue advisories four times each day, starting at 0000 UTC and repeating the process every six hours. Both agencies use information from climatological tropical cyclone forecasting models and estimates a storm's 10-minute maximum sustained winds and its minimum barometric pressure using resources such as the Dvorak technique and numerical weather prediction.
For the majority of the season, an extreme El Niño caused the sea surface temperatures (SST's) in the Pacific Ocean north of the Equator to reach exceptionally high levels. Most of the convection which developed during the year formed south of 30° N; consequently, according to the JMA, Japan, the Korean Peninsula, and most of Mainland China north of Shanghai suffered relatively little impact from the season's storms compared to other regions. Overall, the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season witnessed 30 named storms, six above the long-term average of 24. In addition, 21 of the storms became typhoons , eight above the long-term average of 13. For comparison, the number of storms and typhoons observed during the year are the second and third highest numbers in their respective categories, after 36 storms the 2017 season and 33 storms from the 2019 season, and 31 typhoons in the 2017 season.
The 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season started off completely dormant of tropical cyclone activity until June; this was caused by high amounts of wind shear dominating the Pacific Ocean's waters and preventing any tropical disturbances from forming. However, in June, the turbulent wind shear began relaxing near the Philippines, resulting in the development of Tropical Storm Arno and Severe Tropical Storm Bobbie. Next, in July, wind shear began relaxing across the entire Western Pacific; a further five storms formed, including the deadly Typhoon Faith. By August, the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) moved into the basin, further enhancing tropical cyclone activity. Six storms developed during the month, including the destructive Typhoon Juliet. The MJO continued to reside over the Western Pacific in September, increasing the SST's to levels unlike any other witnessed in 15 years of available records. Seven total storms were observed throughout the month, with two of them, Typhoons Quinn and Sukru, causing unprecedented land impact. Furthermore, in October, an additional eight storms developed; one of the storms was the damaging Typhoon Ulli. This marked the most active October in a Planet X Pacific typhoon season. However, in November, the MJO departed from the basin and SST's significantly cooled down; as a result, only one storm, Severe Tropical Storm Cecelia, formed during the month. Moreover, in December, the inactivity continued as wind shear began picking up and the El Niño conditions began dissipating, with only Typhoon Dieter developing.
Storms[]
In the given storm information below, the wind speeds in storm advisories can differ between that of the JTWC and that of the JMA; this difference is because the JTWC uses 1-minute mean wind criteria to assess a storm's maximum sustained winds, whereas the JMA uses 10-minute mean wind criteria to determine a storm's maximum sustained winds. Consequently, the JTWC's maximum sustained winds for a cyclone can appear to be significantly higher than the JMA's described maximum sustained winds for the same cyclone.
Many of the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season's 30 cyclones had some effect on land.
Tropical Storm Arno (Arnel)[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 11 – June 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 997 hPa (mbar) |
Arno was a short-lived tropical storm that grazed the Philippines. It caused an indirect fatality and $300,000 (2029 USD) in damage across the nation.
Severe Tropical Storm Bobbie (Bayani)[]
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 22 – June 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 993 hPa (mbar) |
Bobbie was a short-lived severe tropical storm that made two landfalls over the Philippines. It resulted in five deaths (two direct, three indirect) and caused $900,000 (2029 USD) in damage across the nation.
Typhoon Coppelius (Crisanto)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 5 – July 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 965 hPa (mbar) |
Coppelius was a moderately intense typhoon that made a landfall over rural Mainland China. Hundreds of landslides killed 45 people, and a further 30 people drowned out at sea. Total losses reached $1.2 million (2029 USD).
Typhoon Desiree[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 9 – July 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 975 hPa (mbar) |
Desiree was a rapidly intensifying typhoon that grazed the Vietnam coastline and ultimately struck southern China just east of Hainan. Two Chinese citizens drowned out at sea when their ship capsized, and seven other people drowned from flash flooding across various regions of southern Mainland China. Total damages of $400,000 (2029 USD) were reported in the wake of Desiree.
Typhoon Emil (Datu)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 16 – July 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 984 hPa (mbar) |
Emil was a short-lived storm that unexpectedly intensified into a typhoon right before its Vietnam landfall. Three fatalities were reported from a car crash in Ho Chi Minh City, and three other deaths occured when a group of surfers were swept out to sea by a rogue wave. Damages from Emil reached $200,000 (2029 USD), particuarly in the Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan area.
Typhoon Faith (Efren)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 26 – August 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 895 hPa (mbar) |
Faith was an erractic typhoon that explosively intensified over the Philippines and later tracked directly over Taipei, Guangzhou, and Shanghai. Six hundred sixty-six people perished during the storm (426 directly, 140 indirectly) because of its heavy precipitation and gusty winds. Damages of $2 billion (2029 USD) were reported across the Philippines, Taiwan, and Mainland China, particuarly on Luzon Island.
Typhoon Gunther (Fermin)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 31 – August 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 988 hPa (mbar) |
Gunther made a landfall over northwestern Vietnam near Hanoi. The system's heavy rain drowned four people walking near a river, left behind $300,000 in losses, and caused moderate damage to the fishing industry located around Hanoi.
Typhoon Hope (Gani)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 4 – August 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 895 hPa (mbar) |
Hope was a long-lived typhoon that made two landfalls, one over Taiwan and the other over China. Significant damage was reported in the Kaohsiung metropolitan region, where apartments were severly damaged, cars were overturned, and glass was blown out of many tall skyscrapers, such as the Tuntex Sky Tower. In Mainland China, many rice fields were flooded, resulting in price inflations. Overall, Hope caused 503 fatalities (337 direct, 166 indirect) and $1 billion (2029 USD) in damage.
Typhoon Ianto (Heherson)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 8 – August 10 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (95 mph) (10-min) 933 hPa (mbar) |
Ianto was a short-lived typhoon that formed unusually close to the equator. It made a landfall over the Philippines and the island of Borneo. Due to the system's abnormal nature, 750 fatalities (258 direct, 492 indirect) and $1.4 million (2029 USD) in losses occured, particuarly in Brunei.
Typhoon Juliet (Isagani)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 13 – August 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 895 hPa (mbar) |
Juliet was a typhoon which executed many cyclonic loops. It made landfalls over the eastern and western Philippines, Vietnam, Taiwan, and Japan. Damages of up to $1.7 billion (2029 USD) were reported, primarily because of agricultural losses; however, only 123 fatalities (81 direct, 32 indirect) occured in relation to Juliet due to warnings being issued in advance of the system by the JMA.
Typhoon Kurt (Jejomar)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 19 – August 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min) 916 hPa (mbar) |
Kurt was a short-lived intense typhoon that affected the Philippines, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, and China. The system's intense precipitation flooded many rural regions of the Indochina Peninsula, and its gusty winds damaged many structures not designed to survive typhoons. Overall, Kurt killed 130 people (60 direct, 70 indirect) and left behind $20 million (2029 USD) in damage.
Typhoon Lucy (Kidlat)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 25 – August 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (95 mph) (10-min) 935 hPa (mbar) |
Lucy, on the heels of Kurt, made a landfall over the Philippines, grazed the southern Vietnam coastline, and made a rare Malaysia landfall. While the only impact on the Philippines and Malaysia from the typhoon was slight precipitation, several landslides were reported in southern Vietnam. Because Lucy did not affect land as severely as Kurt did, only 64 fatalities (59 direct, five indirect) and damages of $5 million (2029 USD) were reported.
Tropical Storm Mattathias (Liberato)[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 30 – September 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 995 hPa (mbar) |
Mattathias was a short-lived tropical storm that did not affect land.
Tropical Storm Noelle[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 2 – September 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 999 hPa (mbar) |
Noelle was a short-lived tropical storm that did not affect land.
Tropical Storm Olaf[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 7 – September 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
Olaf was a short-lived tropical storm that did not affect land.
Tropical Storm Patsy (Melchor)[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 11 – September 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 993 hPa (mbar) |
Patsy was a weak tropical storm which brushed Vietnam and the Philippines. Due to the system's fast motion, only $100,000 (2029 USD) in losses and two fatalities (one direct, one indirect) were reported. However, Patsy dumped excessive rainfall into the Cagayan River, setting the stage for Typhoon Quinn's historic flooding.
Typhoon Quinn (Narding)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 13 – October 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 295 km/h (185 mph) (10-min) 854 hPa (mbar) |
Quinn was an exceptionally intense typhoon that made its landfalls over the Philippines, Vietnam, Hainan, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan. Extremely heavy precipitation flooded many rivers across East and Southeast Asia, such as the Cagayan, Mekong, and Yangtze. The flooding resulted in thousands of deaths, significant damage to structures and vegetation, the colossal obliteration of entire regions, and the loss of millions of valuable objects. Ninety countries worldwide sent preselected citizens to assist homeless people in the wake of Quinn. All in all, the typhoon killed an estimated 300,000 people (roughly 100,000 direct and 200,000 indirect) and left behind $200 billion (2029 USD) in losses.
The extreme damage from Typhoon Quinn was so severe, the JMA, JTWC, PAGASA, China Meteorological Agency (CMA), Hong Kong Observatory (HKO), and Thai Meteorological Department (TMD) all requested that international agencies refrain from using the name Quinn when identifying the typhoon and instead call it the Great Southeast Asia Typhoon of 2029.
Quinn was the first Planet X typhoon to feature triple eyewalls, and it was the longest-lasting storm of the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season.
Tropical Storm Ruby (Pacifico)[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 22 – September 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 1002 hPa (mbar) |
Ruby, the weakest and shortest-lasting storm of the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season, did not affect land. It was rapidly absorbed into the stronger Typhoon Quinn by a Fujiwhara interaction.
Typhoon Sukru (Rizal)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 29 – October 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 240 km/h (150 mph) (10-min) 872 hPa (mbar) |
Sukru was a long-lived, intense typhoon which continued the misery Quinn had begun on the Philippines. The Cagayan River reflooded, damaging shelters containing homeless people, washing away objects that survived Quinn's flooding, and hampering recovery efforts along the nation. Sukru also affected China, indunating rice fields in the country's rural regions and bringing hurricane-force winds to Hong Kong. Overall, the typhoon resulted in 40,000 fatalities (approximately 25,000 direct, 15,000 indirect) and $3 billion (2029 USD) in losses.
Tropical Storm Tilda[]
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 30 – October 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 989 hPa (mbar) |
Tilda was a long-lived tropical storm that made a landfall directly over Yokohama. It drowned two fisherman, swept another person out to sea, left behind $40,000 (2029 USD) in losses, and caused a landslide near Kobe.
Typhoon Ulli (Sherwin)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 3 – October 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 275 km/h (170 mph) (10-min) 864 hPa (mbar) |
Ulli was an intense typhoon which explosively intensified before making a landfall in the northeastern Philippines. Thousands perished during the storm's onslaught and agricultural and structural damage was very severe. However, because Quinn, Sukru, and Ulli occurred only weeks apart, it is impossible to determine how much impact Ulli caused by itself in the nation. In Macao, many casinos were damaged or destroyed by the typhoon, and severe looting was reported in the system's aftermath. Nearby, in Hong Kong, gusty winds knocked many glass panels off of skyscrapers and sunk ships in Victoria Harbor. Elsewhere, in Mainland China, dozens of landslides resulted in numerous fatalities and property losses. Collectively, Ulli caused approximately 7,000 deaths (roughly 4,000 direct, 3,000 indirect) and $1.1 billion (2029 USD) in damage.
Typhoon Vera[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 4 – October 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min) 895 hPa (mbar) |
Vera was a long-lived typhoon which affected Japan, South Korea, and Mainland China. Its arrival on Japanese territory surprised many locals, as the nation had escaped most of the season's destructive storms up to this point in the season. Consequently, many homes were damaged by floodwaters, drowning hundreds, and homelessness became a very severe issue in major cities. However, in Seoul, Incheon, and various other South Korean cities, aside from heavy rainfall runoff, Vera's impact was not as severe. On the contrary, Mainland China received heavy impact from the typhoon. Rapid precipitation indunated farming fields and city streets from floodwaters, preventing any transportation for days. Vera's recovery process in Mainland China was compunded by Typhoon Benjamin, Severe Tropical Storm Cecelia, and Typhoon Dieter, which all hit the same region within a few months of the storm's attack. In conclusion, Typhoon Vera resulted in 654 fatalities (462 direct, 192 indirect) and $70 million (2029 USD) in losses.
Typhoon Wilbur[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 7 – October 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 921 hPa (mbar) |
Wilbur was a short-lived typhoon that did not result in any fatalities; however, its remnants brought gusty winds to the Japanese island of Honshu, leaving behind total damages of $4,000 (2029 USD).
Typhoon Xandra[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 9 – October 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 982 hPa (mbar) |
Xandra was a short-lived typhoon which did not affect land.
Typhoon Yoda[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 12 – October 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min) 960 hPa (mbar) |
Yoda was a short-lived, rapid-intensifying typhoon that did not affect land.
Severe Tropical Storm Zita[]
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 16 – October 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 987 hPa (mbar) |
Zita was a moderately intense severe tropical storm that did not affect land.
Typhoon Antoinette (Virgilio)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 25 – November 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min) 918 hPa (mbar) |
Antoinette was an intense typhoon which made two landfalls over the Philippines and a single landfall over Vietnam. In Vietnam, impact from the system was limited to heavy rainfall and several widespread landslides. However, in the Philippines, the damage was much greater because Antoinette made its second landfall directly over Manila. Strong winds knocked down light poles, trees, and numerous other structures, crushing cars, traffic lights, mobile homes, and various other weak objects. Hundreds of boats in Manila Bay were hurled ashore by rouge waves from the typhoon. Elsewhere, in Central Luzon and the Cagayan Valley, severe flooding caused dozens of reported drownings, although the impact was far less than what was observed in the Manila city proper. Overall, Antoinette caused 1,143 fatalities (765 direct, 378 indirect) and $90 million (2029 USD) in losses.
Typhoon Benjamin (Arvin)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 30 – November 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min) 962 hPa (mbar) |
Benjamin was a moderately intense typhoon that made a landfall in Mainland China just north of Shanghai. Causing additional flooding and property damage in the same region Vera had struck only a few weeks earlier, the typhoon killed 325 people (231 direct, 94 indirect) and left behind $125 million (2029 USD) in damage.
Severe Tropical Storm Cecelia (Benjie)[]
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 15 – November 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 975 hPa (mbar) |
Cecelia was a long-lived severe tropical storm which made landfalls over Hainan, Macao, Taiwan, and Mainland China. Due to the system's fast pace, relatively minimal impact was reported, although minor flooding from a storm surge occurred in Northeastern China, which was already affected by Typhoons Vera and Benjamin. Collectively, Cecelia caused four fatalities, all of which were direct, and losses of $400,000 (2029 USD).
Typhoon Dieter (Danilo)[]
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 21 – December 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 958 hPa (mbar) |
Dieter was a moderately intense typhoon which grazed the eastern Philippine coastline, made a direct hit on the city of Taipei, and then directly attacked Shanghai. Thousands of plane flights in and out of Shanghai Pudong International Airport were cancelled, many rice fields overflooded, and in Mainland China, whole roads were swept away by rising floodwaters. In addition, an additional amount of impact from Dieter occured in the region of Northeastern China already severly affected by Vera, Benjamin, and Cecelia. Hundreds of homes were destroyed by the heavy precipitation from the typhoon, and agricultural losses were beyond exceptional. Damage from Dieter is estimated at $150 million (2029 USD) and 97 deaths (53 direct, 44 indirect) were reported.
Storm names[]
Within the tropical cyclone responsibility boundaries of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, the JTWC assigns names to storms that develop within the basin. Moreover, PAGASA also assigns names to Western Pacific tropical cyclones. Therefore, one single storm can have a name assigned to it by both the JTWC and PAGASA. On the behalf of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)'s Typhoon Committee, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center's Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) Honolulu assigns preselected international names to tropical cyclones, should it be judged to have attained 1-minute maximum sustained winds of 65 km/h (40 mph). PAGASA assigns a name to a tropical cyclone should it form or move into their area of responsibility, which encompasses a rectangular box spanning from 135°E to 115°E and between 5°N to 25°N, regardless of whether or not the storm has been assigned an international name. Should a tropical cyclone cause significant impact, its name will be retired by the Typhoon Committee, or PAGASA if it is a Philippine name. Also, in the scenario in which all the PAGASA names allocated for the season are used, as what occured during this season, extra names will be taken from an auxiliary list, which is published before the start of the year.
International names[]
See also: Lists of tropical cyclone names and Tropical cyclone naming
Tropical cyclones forming during the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season were named from the following lists by the RSMC in Honolulu, Hawaii, once they reached tropical storm intensity. This year marked the first time these lists were used. In previous years, from 2016 to 2028, two naming lists consisting purely of masculine names were used; however, various protests from men's rights groups forced the JTWC to change their naming lists. Many of the names were submitted by the United Kingdom Met Office.
|
|
|
|
|
Philippines[]
PAGASA uses its own naming scheme to identify storms that form or move within their area of responsibility. Similar to the international names, this year was the first occasion in which this naming list was used. All names on this list are the names commonly given to Filipino males and were submitted by various locations across the Philippines. Because the naming list was insufficient for the season, three names from an auxiliary list were used. The names that were not retired after this season were used again in the 2033 Planet X Pacific typhoon season.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retirement[]
See also: List of retired Pacific typhoon names (JMA) and List of retired Philippine typhoon names
Shortly after the conclusion of the 2029 Planet X Pacific typhoon season, the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee retired the names Faith, Hope, Juliet, Quinn, Sukru, Ulli, and Antoinette. Their replacement names for future usage will be Frieda, Helene, Jewel, Quirikas, Sigmund, Usman, and Amelie, respectively.
Also, PAGASA announced the retirement of the names Efren, Heherson, Narding, Rizal, Sherwin, and Virgilio, as all of the listed names identified storms which either caused 300 fatalities or $1 billion pesos (PHP) in losses. For the 2033 season, their replacements will be Erwin, Homobono, Nimuel, Rodel, Sayen, and Vaughn, respectively.
See also[]
- 2017 Planet X Pacific typhoon season - A similarly active and destructive Planet X typhoon season.
- Planet Earth typhoon seasons
External links[]
NOTE: All links below relate to Planet Earth weather warning centers and resources.
- Japan Meteorological Agency
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center.
- China Meteorological Agency
- National Weather Service Guam
- Hong Kong Observatory
- Macau Meteorological Geophysical Services
- Korea Meteorological Agency
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
- Taiwan Central Weather Bureau
- Digital Typhoon - Typhoon Images and Information
- Typhoon2000 Philippine typhoon website
| 2020-29 Planet X Pacific typhoon seasons |
|---|
| Previous: 2019 - 2020 - 2021 - 2022 - 2023 - 2024 - 2025 - 2026 - 2027 - 2028 - 2029 - Next: 2030 |